Adjusted energy intensities
- After adjusting for differences in general price levels, by converting GDP at purchasing power parities (ppp), final intensities decrease for countries with low prices (such as the central-eastern or southern countries). For example, in Bulgaria, Romania, Poland and Hungary the adjusted intensity is about 40% lower than the observed intensity; in Lithuania, Croatia, Czechia, Slovakia and Latvia it is more than 30% lower than the observed intensity.
- After adjustment, the gap between EU countries is significantly reduced.
Final energy intensities at ppp in 2023 (normal climate)
- Some of the observed differences in final energy intensity levels after ppp corrections can be further adjusted to account for some other quantifiable national characteristics, such as climate and the structure of economic and industrial activities. The adjustment to the average economic structure and climate of the EU makes the comparison of final energy intensities more meaningful and reduces the gap between countries.
- Malta, Romania, Netherlands and Portugal have the lowest adjusted energy intensities, below 0.06 koe/EUR2015ppp.
Final energy intensities adjusted at ppp and EU average structure and climate (2023)
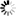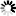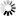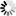
Note : some countries are missing due to incomplete data on value added by industrial sector.





